Explore AMM
2 AMM tokens listed on Mango
Understanding AMMs
An Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a decentralized protocol for crypto trading. AMMs use smart contracts and algorithms to automatically facilitate trading and liquidity provision.
The key characteristic of an AMM is that it relies on liquidity pools rather than order books. Liquidity providers deposit pairs of tokens into these pools to create trading pairs. The ratio of the two tokens in the pool determines the price. Users can then trade one token for another by interacting directly with the smart contract.
The most common algorithm used by AMMs is the constant product formula, popularized by Uniswap. The formula is expressed as:
x*y=k
- x and y are the quantities of the two tokens in a liquidity pool.
- k is a constant value, ensuring that the product of x and y remains the same before and after a trade.
When a user makes a trade the individual quantities of the two tokens change (one goes in and one goes out). This change in token quantities maintains the balance in the pool and determines the price between the two tokens.
When plotted on a chart, the outcome is a hyperbolic curve. Liquidity for both assets is always available but at progressively higher prices.
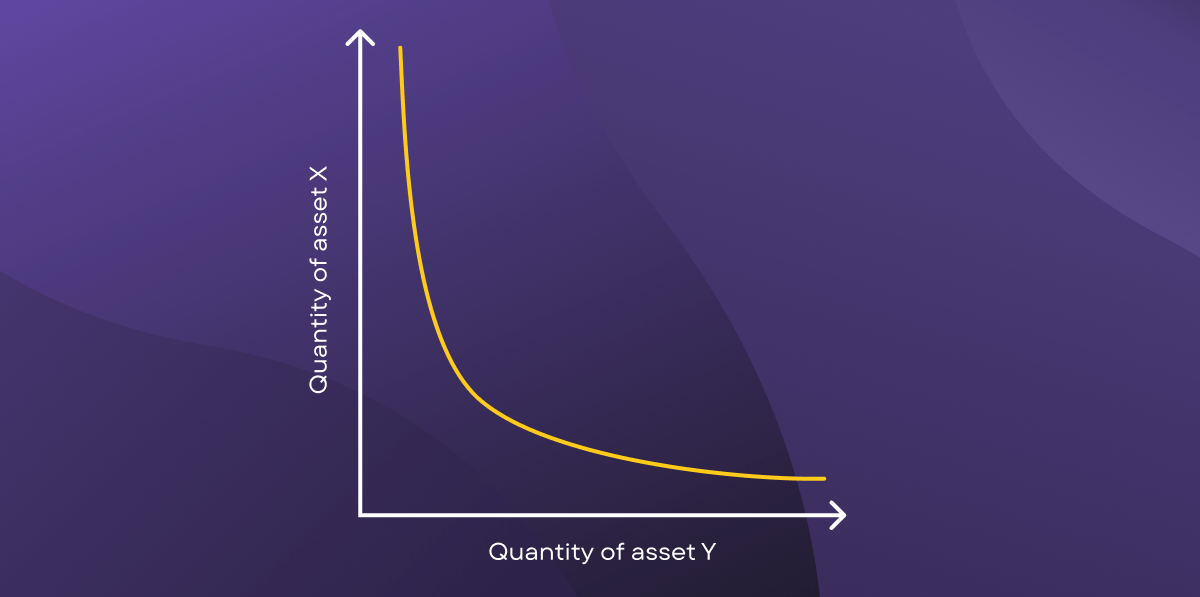
Visualization of the constant product formula
Problems with AMMs
Whilst AMMs have revolutionized decentralized finance they come with their own set of issues. Here are some key problems with AMMs:
Capital inefficiency
Capital efficiency is essential to maximize the benefits for liquidity providers and traders. It ensures funds are generating returns. In highly liquid AMM pools, a substantial portion of funds may remain unused due to narrow price movements. This results in low capital efficiency.
Impermanent loss
Liquidity providers in AMMs are exposed to impermanent loss. This happens when the value of the provider's holdings in the pool is less than if they had simply held the tokens without providing liquidity. It's caused by the number of tokens returned from the pool being different from what was initially supplied.
Front running
Front running is where traders exploit the time delay between transaction submission and blockchain confirmation to gain an unfair advantage.
Market manipulation
The design of AMMs makes them susceptible to market manipulation. Price is determined by the ratio of assets in the liquidity pool, which can be impacted by large trades in and out of the pool.
Smart contract risks
AMMs rely on smart contracts and any vulnerabilities or bugs in these contracts pose potential security risks and financial losses.
Lack of control over pricing
Liquidity providers have limited control over asset pricing in AMMs, leading to underutilized and poorly provisioned liquidity that affects both providers and traders.
Traders and liquidity providers must be mindful of these challenges when engaging with AMMs.
AMMs on Solana
AMMs are not unique to Ethereum and Solana has many AMM protocols. The two most prominent are Orca and Raydium.
Orca
Orca is a Solana DEX built around a Concentrated Liquidity Automated Market Maker (CLAMM) model. The idea behind CLAMM is to enhance capital efficiency within a liquidity pool by minimizing slippage.
Traders on Orca can swap tokens and add liquidity to any of their liquidity pools to earn a share of trading fees.
Trade Orca on MangoSwap or trade up to 5x leverage. Earn interest on deposits or borrow.Swap ORCATrade ORCA
Raydium
Raydium is also a Solana DEX that allows traders to swap tokens within liquidity pools. The protocol determines the best route across all pools to provide the best price.
Raydium's AMM also interacts with OpenBook DEX's central limit order book (CLOB), allowing pools to access the order flow and liquidity on OpenBook, and vice versa. This counters some of the problems with traditional AMMs.
Raydium also offers features such as an order book AMM and permissionless liquidity creation (liquidity pools can be created for any token pair).
Trade Raydium on MangoSwap or trade up to 5x leverage. Earn interest on deposits or borrow.Swap RAYTrade RAY
The data displayed on this page is provided for informational purposes only. It may be delayed and is not guaranteed to be accurate. It is not intended for trading or investment purposes. The platform does not assume any responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of the data, and shall not be liable for any errors, omissions, or any losses resulting from its use.
Do not invest unless you are prepared to lose all the money you invest. Crypto is a high-risk investment and you should not expect to be protected if something goes wrong.